Quotations
Thought for Us
Imagination is more important than knowledge
The Buchalter Cosmology Prize was conceived on the premise that there are still fundamental gaps in our understanding of cosmology and that currently-accepted paradigms such as inflation and dark energy are incomplete, and possibly even incorrect descriptions of our Universe. It was created to stimulate ground-breaking theoretical, observational, or experimental work in cosmology that challenges, extends, or illuminates current models and/or helps explain the cosmic expansion from first principles. The ultimate goal is to help spur the formulation of a broader cosmological theory that explains current observations, puts forth testable new predictions, and fundamentally advances our understanding of physics. The Cosmology Prize will be awarded in January 2018
Today, cosmology is based on Einstein's expanding Universe beginning with Hubble's discovery of an expanding Universe from redshift measurements of receding galaxies. The notion of dark matter evolved because Newton's mechanics could not explain how clusters of galaxies are held together under the high velociites inferred by measurements of redshift. For a brief history of dark matter see PressRelease
The instant Buchalter Cosmology paper argues cosmic dust causes galaxy velocities inferred by redshift measurements to be overstated, and if corrected for cosmic dust would show clusters of galaxies are held together by Newtonian mechanics. What this means is the Universe is not expanding, but rather is indeed static and dynamic as Einstein once thought. See Paper.

Thermal fluctuations although valid for macroscopic structures based on the FDT of electrodynamics including the formation of evanescent waves are shown invalid at the nanoscale as the Planck law of QM precludes the atoms in NS from fluctuating in temperature. FDT stands for fluctuation dissipation theorem, QM for quantum mechanics, and NS for nanostructures. Unlike the conservation of heat at the macroscale by raising the temperature, QM requires the conservation of heat at the nanoscale to proceed by creating EM radiation within NS. See Abstract and Presentation

The manipulation of flow in nanochannels by charge is thought confirmed by numerous MD simulations of flow by single file of molecules interacting with the interior of CNTs through L-J potentials. MD stands for molecular dynamics, CNT for carbon nanotubes, and L-J for Lennard-Jones. However, MD simulations have anomalous findings: The flow can be stopped by placing a static positive charge near the outside of the CNT suggesting the the flow is somehow charged. Moreover, vibrating the charge can increase the flow. Vibrating charge shows flow is maximum at NIR frequencies suggesting the breakage of hydrogen bonds with CNT walls having energies of 20 kJ/mol. NIR stands for near infrared. However, experiments confirming the validity of the MD model of molecules suspended on hydrogen bonds do not exist. Regardless,
Since nanochannel cross-sections have at least one dimension < 100 nm, the molecules upon entering the nanochannel are exposed to EM radiation originating because QM precludes the heat from the surroundings from being conserved by raising the temperature of the nanochannel. QM stands for quantum mechanics. Indeed, the wavelength of the EM radiation standing across the < 100 nm dimension of the nanochannel is < 200 nm having Planck energy > 6 eV which is sufficient to remove electrons from atoms in most molecules including the inside surface of the CNT wall.
What this means is the hydrogen bonds do not break by the flow, but are broken by EM radiation, the electrons removed by the photoelectric effect leaving a flow of positive charged atoms with the CNT surface also charged positive. Nanochannel flow is therefore significantly enhanced above classical Hagen-Poiseuille theory because Coulomb repulsion between the atoms as well as the CNT wall avoids frictional contact and therefore viscosity vanishes with the flow of positive charged atoms approaching a frictionless condition bounded by the Bernoulli equation. MD simulations are performed for a single-file flow of positive charged atoms that show water flow in CNTs can be manipulated with static and vibrational positive charges. See Paper and Presentation An Audio MP3 file of the PPT Presentation is available. Open both in separate windows and follow the PPT with the Audo file.
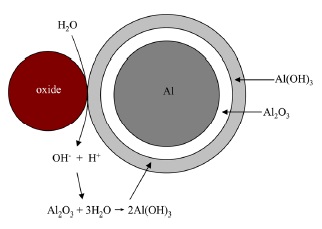
Hydrogen is a clean and renewable energy source, but requires a cost-effective method of storage and transport suggesting a mobile system where the hydrogen is generated directly from water at the point of use. Recently, a H-Al system has attracted considerable attention. H-Al stands for hydrogen-aluminum. However, a passive Al2O3 film develops on Al surfaces upon exposure to water that inhibits the hydrogen production. Methods directed to the disruption of the Al2O3 film have been proposed for hydrogen generation using Al with water.
In the uniform corrosion model, the Al2O3 film is thought disrupted by hydration when 22 nm NPs of TiO2 are added to the water. NPs stand for nanoparticles. The thumbnail shows a TiO2 NP contacting an Al particle coated with a Al2O3 film. Water is shown to dissociate into H+ and OH- ions, the highly reactive OH- ions combining with the Al2O3 film to produce the intermediary Al (OH)3 that disrupts the Al2O3 film. Alternatively, the Al (OH)3 was directly synthesized into NPs of 50-90 nm diameter x 10 nm thick platelets.
The problemis the uniform corrosion mode does not explain how the TiO2 and Al (OH)3 NPs dissociate water into H+ and OH- ions, the dissociation requiring at least EM radiation in the UV of about 5 eV. Until then, the corrosion model must be considered questionable.
In this regard, the source of hydroxyl OH - ions in the uniform corrosion model is proposed to be the catalytic action of TiO2 and Al (OH)3 NPs in producing EM radiation that lowers the activation energy to disrupt the Al2O3 film. A similar situation arises in the creation of UV radiation upon the IR heating of silicate NPs in water producing steam without boiling. See Press Release
Physically, NPs do not naturally emit UV, but TiO2 and Al (OH)3 NPs do convert heat from the surroundings into UV radiation if the heat capacity of the NPs somehow vanishes. Classically, NPs have heat capacity, but QM differs as the heat capacity of the atom given by the Planck law does indeed vanish under high EM confinement. QM stands for quantum mechanics. But high EM confinement is inherent in NPs upon absorbing heat because their high S/V ratios confine the heat to the NP surface. S/V stands for surface-to-volume. NP atoms are therefore placed under high EM confinement and their heat capacity vanishes. Lacking heat capacity, the heat may only be conserved by a non-thermal mechanism suggested here as simple QED.
Simple QED differs from the complex theory advanced by Feynman in that heat is conserved in NPs by creating non-thermal EM radiation standing across the NP diameter d as the heat adjusts to the EM confinement bounded by the NP surface. Hence, the EM radiation has half-wavelength λ/2 = d. The speed of light c corrected for the refractive index n of the NP gives the Planck energy E = h(c/n)/ λ = hc/2nd.
In application, the titanium dioxide TiO2 NPs having d = 22 nm and n = 2.5 gives 2nd = 110 nm. The absorption of 110 nm EM radiation in water is high as shown below inthe absorption spectrum for water. Water is therefore dissociated and hydroxyl ions are available to disrupt the Al2O3 film .
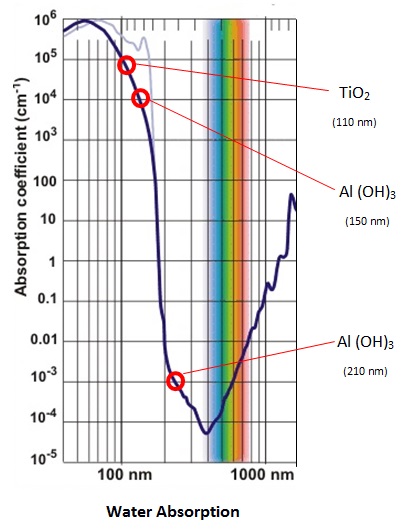
The Al (OH)3 NPs as platelets differ from the near spherical TiO2 NPs in that all dimensions difffer. Consistent with conserving heat in minimum time, simple QED dissipates EM radiation in the mode of the highest frequency which corresponds to the 10 nm thickness direction. But after synthesis, the platelets are generally attached by their flat sides to Al particles, and in effect, the high frequency EM radiation is quenched, and therefore the direction of EM dissipation is across the platelet diameter. Taking the average diameter d = 70 nm and n = 1.5 gives 2nd = 210 nm, but as shown above the absorption in water is low and OH - ion production is inefficient. However, at d = 50 nm, 2nd = 150 nm and the absorption is high , and therefore water is efficiently dissociated with OH - ions available to disrupt the Al2O3 film. See Press Release
In conclusion, the uniform corrosion model that relies on a source of hydroxyl OH- ions to disrupt the Al2O3 film is supported by the catalytic action of TiO2 and Al (OH)3 NPs that convert heat in the surroundings into EM radiation to dissociate the water molecules, and
The TiO2 and Al (OH)3 NPs do not change during the Al–water reaction, indicating that they are in fact true catalysts to assist the reaction of Al with water.

Engaging the public with astronomy and space science research is difficult because complex explanations by scientific experts are not understood by the common person. This is especially relevant in cosmology where astronomers claim dark matter exists having a mass about 5 times that of what we observe on Earth, but is invisible and cannot be observed! Because of the unusual and perhaps bizarre nature of dark matter claims, it is only natural for the public to question whether the astronomy community is taking advantage of the taxpayer who is paying for meaningless research.
Nevertheless, astronomers do admit there are still fundamental gaps in our understanding of cosmology and that currently accepted paradigms such as dark matter are incomplete and perhaps even incorrect descriptions of our Universe. Consistent with the scientific background of the public, my paper is not complex theoretical work and can be understood with knowledge of basic physics with deductions from the well-known Planck law of quantum mechanics formulated over a century ago. I argue that Hubble overstated the expansion of the Universe based on velocities inferred from the redshift of light from receding galaxies because Hubble's measurements included an additional redshift as the light is absorbed by the intervening cosmic dust on its way to the Earth. Because the overstated velocities were significant, astronomers concluded invisible dark matter must be present to hold the Universe together.
Regardless, my challenge to current cosmology is based on first principles that can be confirmed by experiment and understood by the public thereby refuting over nearly a century of erudite, but otherwise erroneous explanations of dark matter by the astronomy community.
Since Hubble, astronomers based on classical physics have claimed the light from distant galaxies upon absorption raises the temperature of cosmic dust. But the dust is nanoscopic and governed by quantum mechanics, the Planck law of which shows cosmic dust cannot conserve galaxy light by raising temperature because its heat capacity vanishes. Conservation therefore proceeds as the galaxy photon upon absorption readjusts to fit inside the dimensions of the dust nanoparticle. Depending on the refractive index and diameter of the nanoparticle, a redshifted galaxy photon is re-emitted. Regardless, cosmic dust redshift has been verified in numerous Earth based experiments showing nanoparticles redshift laser light. To avoid overstated galaxy velocities in the future, corrections are provided to determine if the measured redshift is indeed caused by a receding galaxy velocity or from cosmic dust. Historical observations in astronomy are discussed including the resolution of the long-standing galaxy rotation problem without the need for dark matter if the redshift measurements giving the higher than expected galaxy velocities are corrected for the redshift in cosmic dust. Similarly, an accelerating Universe expansion need not exist if the redshift showing supernovae brighter than expected is corrected for the redshift in the intervening dust. The Sunyaev-Zel’dovich Effect,Tolman test, exoplanets, and Olbers paradox are briefly discussed. See Abstract

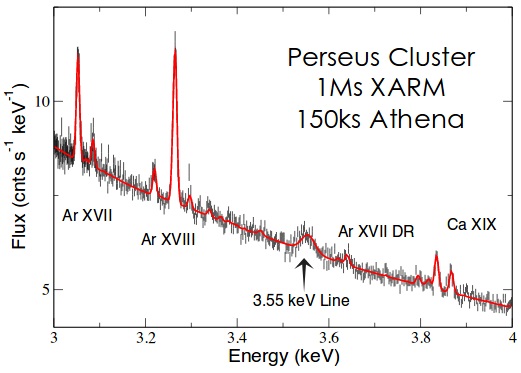
In 2014, a mysterious 3.5 keV X-ray emission from the Perseus galaxy was found that could not be explained by standard X-ray wavelengths of atomic elements. The X-ray emission from the Perseus galaxy is shown above. Subsequently, the 3.5 keV signal was found in 73 other galaxies suggesting uniformity of the signal throughout the cosmos. Since the X-ray signal is not present in the known X-ray emission lines of the elements, a dark matter explanation based on sterile neutrinos that upon decay emitted the mysterious X-ray line. However, dark matter decay was ruled out based on incompatibility with expected dark matter distributions.
As of 2016, there was no consensus opinion on the physics behind 3.5 keV signal. Of relevance, charge exchange of bare sulfur atoms stripped of all electrons in the heat of the hot galaxy medium was shown to produce the 3.5 keV X-ray line upon combining with atomic hydrogen in the transition to the ground state. The bare sulfur atoms were prepared by heating CS2 with an electron beam to a minimum energy of 3494 eV.
The proposal here differs in that the 3.5 keV X-rays found in Perseus are produced by simple QED – a far simpler theory than that of Feynman. Simple QED is a consequence of QM that by the Planck law requires the heat capacity of NPs to vanish under high EM confinement. QM stands for quantum mechanics. Since QM denies the atoms heat capacity, the heat does not increase NP temperature. But NPs have high S/V ratios where the heat is absorbed almost entirely in the NP surface. S/V stands for surface-to-volume. Precluded from thermal expansion, surface heat places internal NP atoms under the high EM confinement necessary by the Planck law for heat capacity to vanish. Heat is conserved by creating non-thermal EM standing photon inside the NP having half-wavelength λ/2 = d, where d is the NP diameter. The speed of light c corrected for the refractive index n of the NP gives the energy E of the standing photon, E = h(c/n)/λ = hc/2nd.
Simple QED was origninally formulated for NPs < 100 nm having EUV energy levels. In the extension to X-rays, the NPs are required to fragment to atoms upon heating in the hot galaxy medium. Thermal vaporization does not occur as temperatures do not increase. The heat produces EM radiation that ionizes the NPs and induces Coulomb repulsion that by fragmentation progressively creates smaller clusters until atoms alone are formed. Like a two energy state atom separated by 3.5 keV, the heat then raises the energy level of the atoms to 3.5 keV levels at which time the X-ray is emitted.
In conclusion, applying simple QED to the 3.5 keV X-ray emission from Perseus, the wavelength λ = hc/E = 0.354 nm. The atom diameter d = λ/2n, but at X-ray frequencies, n = 1 and d = λ/2 = 177 pm with radius 88.7 pm. Of the atomic elements, both krypton an sulfur have radii = 88 pm. Krypton aside, simple QED emission is analgous to the charge exchange experiment [2,3] for bare sulfur atoms with the heat provided by the hot Perseus medium instead of electron beams and does not require collisions with H atoms. See Press Release
Simple QED suggests dark matter has nothing to do with the 3.5 keV X-rays. In fact, simple QED shows the recession velocities of galaxies are highly overstated by the redshift of galaxy photons upon interacting with NPs of cosmic dust surounding the galaxy. Indeed, if the measured redshift is corrected for the redshift in cosmic dust, there is no need for dark matter to explain an expanding Universe or the rotation curves in spiral galaxies suggesting the Universe is dynamic, but otherwise static and infinite. See Press Release
Simple QED energy levels differ from conventional QM levels by dependence on the size of the NP or atom that defines the EM energy of the standing wave. With atoms, the simple QED energy levels are in the X-ray regime. However, for the larger NPs, EUV levels are excited. Plasmon resonances thought to characterize NPs are NOT directly excited. Rather, the simple QED levels of NPs in the EUV excite the plasmon resonance by fluorescence.
A quantum state without electron levels?
Electrons in atoms make transitions in electron energy levels by emitting photons with an energy exactly equal to the difference between the two energy levels. But X-ray lines at 3.5 keV do not appear in X-ray emission of atomic elements. What this means is the 3.5 keV X-ray is emitted by a quantum state independent of electron energy levels.
The 3.5 keV X-rays found in Perseus are produced by simple QED, but not the complex theory of Feynman. Simple QED is a consequence of QM that by the Planck law requires the heat capacity of NPs to vanish under high EM confinement. Since QM denies atoms heat capacity, the heat does not increase NP temperature. But NPs have high S/V ratios that require heat to almost entirely reside in the NP surface. S/V stands for surface-to-volume. Precluded from thermal expansion, the surface heat places internal NP atoms under the high EM confinement necessary by the Planck law for the heat capacity of the atom to vanish.
Without an 3.5 keV electron energy level, the simple QED transition from the ground state to 3.5 keV is created by using up the heat in the NP surface depending only on the dimensions of the NP that define the energy of the photon standing within the EM confinement. Provided the heat is deposited promptly, say < 150 fs, energy conservation proceeds by creating a non-thermal photon inside the NP having half-wavelength λ/2 = d, where d is the dimension of the NP diameter. The Planck energy E of the standing photon is, E = hν = h(c/n)/λ = hc/2nd, where c is the speed of light and the refractive index n correcting for the lower speed in the NP. Lower frequency UV-VIS states of the NP including plasmon resonances are excited from simple QED by florescence and in the absence of lower NP states the photon is directly emitted to the surroundings.
Simple QED was formulated for NPs > 10 nm having EUV energy levels - not atoms < 1 nm in the X-ray range. In the extension to 3.5 keV X-rays, cosmic dust NPs in Perseus are required to fragment to bare atoms upon heating in the hot galaxy medium. Thermal vaporization does not occur as QM precludes high temperatures. Instead, the heat produces EM radiation that ionizes the NPs inducing Coulomb repulsion that by fragmentation progressively creates smaller and smaller clusters until atoms alone are formed. Depending on the atom diameter, the heat by simple QED raises the energy level of the atoms at which time the 3.5 keV X-ray is emitted.
In applying simple QED to the 3.5 keV X-ray emission from Perseus, the above spectra shows E = 3.55 keV giving the wavelength λ = hc/E = 0.349 nm. The atom diameter d = λ/2n, but at X-ray frequencies, n = 1 and d = λ/2 = 174.5 pm with radius 87.25 pm. Of the atomic elements, krypton and sulfur have radius = 88 pm. Krypton aside, simple QED emission is analogous to the charge exchange experiment [2,3] for bare sulfur atoms with the heat provided by the hot Perseus medium instead of Earth based electron beams. Collisions with H atoms are not required. The line broadening of the 3.55 keV line is caused by small variations in the dimensions d of the fragmented sulfur atom. See Press Release
Simple QED suggests dark matter has nothing to do with the 3.5 keV X-rays. In fact, simple QED shows the recession velocities of galaxies are highly overstated by the redshift of galaxy photons upon interacting with NPs of cosmic dust surrounding the galaxy. Indeed, if the measured redshift is corrected for the redshift in cosmic dust, there is no need for dark matter to explain an expanding Universe or the rotation curves in spiral galaxies suggesting the Universe is dynamic, but otherwise static and infinite. See Press Release
Simple QED energy levels differ from conventional QM levels based on electron energy levels by dependence on the size of the NP or atom.

In 1926, Hubble’s redshift measurements of light from distant galaxies changed the long-standing paradigm of a static and infinite Universe governed by Newtonian mechanics to a finite and expanding Universe following Einstein’s general relativity, or GR. In the 1970’s, Vera Rubin’s redshift measurements of galaxy rotation curves showed a flat velocity profile in contrast to decreasing velocities predicted by Kepler’s law, the high velocities suggesting dark matter had to be present to hold the galaxies together. Recently, Andrei Maeder proposed GR should be modified by scale invariance allowing high rotational galaxy velocities without the need for dark matter to hold the galaxies together. But scale invariant GR requires the large scale Universe to be empty space without mass which certainly is not self-evident, and in fact can only be erroneous because of cosmic dust. See Press Release
In this regard, an alternative theory of the Universe is proposed : An expanding Universe and dark matter do not exist if the respective recession and rotational velocities of galaxies are corrected for the redshift in galaxy light upon interaction with cosmic dust on its way to the Earth.
Historically, the redshift in cosmic dust went unnoticed for almost a century because galaxy light was assumed to follow classical physics by conserving the galaxy photon by an increase in temperature. But the heat capacity of the atom given by the Planck law of QM, although finite at the macroscale vanishes at the nanoscale, QM standing for quantum mechanics. Conservation of the galaxy photon in dust is therefore only possible by a non-thermal mechanism proposed here to be simple QED, but is far simpler than that proposed by Feynman and others.
Simple QED relies on the high S/V ratio at the nanoscale where the galaxy photon of wavelength λ is absorbed almost entirely in the dust surface. S/V stands for surface to volume. Dust atoms are placed under the high EM confinement necessary for the heat capacity to vanish and a temperature increase does not occur, i.e., the surface heat cannot be relieved by thermal expansion. A non-thermal standing photon having half-wavelength λo/2 = d is then created as the galaxy photon energy adjusts to the EM confinement bounded by the dust surface. The speed of light c corrected for the refractive index n of the dust gives the energy E of the redshift photon, E = h(c/n)/λo for a wavelength 2nd and redshift Z = (2nd - λ)/λ. Once the energy of the galaxy photon absorbed in the dust surface is expended to form the standing photon, the EM confinement vanishes and the galaxy photon now redshifted is free to travel to the Earth.
In cosmic dust, the redshift Z for Lyman - alpha galaxy photons is shown to approach the speed of light to significantly overstate recession and rotation velocities. However, by correcting galaxy redshifts for cosmic dust, not only does dark matter not exist, but both GR and scale invariant GR are irrelevant as galaxy dynamics follows Newtonian mechanics inherent in a static and infinite Universe . See Abstract
and Presentation
An MP3 Audio file of the presentation is available. Open the Presentation PPT and Audio files in separate windows and manually adjust the PPT file to follow the Audio file.

Nanotechnology in the science of the very small and the search for dark matter in the very large Universe may appear to be unrelated, but in fact find commonality in the NPs in Earth based nanotechnology. NPs stand for nanoparticles. NPs are known to conserve heat by emitting EM radiation instead of increasing in temperature because the Planck law of QM requires the heat capacity of the quantum sized NPs to vanish. QM stands for quantum mechanics.
In 1926, Hubble discovered the Universe was expanding based on redshift measurements of light from recessing galaxies. But cosmic dust NPs of mostly silicates permeate the Universe. Upon the NPs absorbing the galaxy light on the way to the Earth, an additional redshift above the Hubble redshift occurs. Recession velocities were therefore overstated to the extent that to hold clusters of galaxies together then dark matter is thought necessary to exist. But if the Hubble redshift is corrected for cosmic dust, dark matter need not exist as the galaxy clusters are held together by Newtonian mechanics.
Because of the ubiquity of cosmic dust, all astronomical velocity measurements based on Hubble redshift are most likely overstated, e.g., the long-standing galaxy rotation problem may be resolved without the need for dark matter if the redshift velocities are corrected for cosmic dust. Similarly, an accelerated expansion of the Universe based on redshift of supernovae recessions need not exist if corrected for the overstated redshifts in intervening cosmic dust.
The problem is astronomers relied on classical physics that allows the atoms in quantum sized dust NPs to have the heat capacity to fluctuate in temperature, the consequence of which has misdirected cosmology into claiming we live in an expanding Universe. Contrarily, QM argues the Universe is not expanding suggesting cosmology return to Einstein’s once upon a time notion of a static and dynamic Universe. Futile searches for dark matter should be discontinued in favor of redshift measurements in cosmic dust under Lyman radiation. See Abstract and Presentation
An MP3 Audio file of the presentation is available. Open the Presentation PPT and Audio files in separate windows and manually adjust the PPT file to follow the Audio file.

Almost a century ago, Hubble’s redshift measurements of light from distant galaxies marked the beginning of the notion that the Universe was expanding thereby supporting Einstein’s GR theory, althouigh dark matter itself was not identified as the consequence of GR, GR stands for general relativity. In 1933, Fritz Zwicky made claimed there was more matter in the universe than what was visible, the so-called dark matter. It was not until the 1970's that Vera Rubin hinted that dark matter might explain how spiral galaxies could stay together under the high rotation velocities. Like Hubble, Rubin inferred galaxy velocities from redshift of galaxy light.
However, Andrei Maeder recently made the controversial proposal that GR modified for scale invariance allows spiral galaxies to have the high rotationl velocities without the need for dark matter to hold the galaxies together. But scale invariant GR requires the large scale Universe to be empty space without mass – an unrealistic condition, let alone unverifiable by the scientific method. See summary Dark Matter is not dead and Critical review of scale invariance
An alternative Dark Matter theory in the negative that has been indirectly verified in nanotechnology is the redshift of laser light by NPs and recently was proposed to CERN as a comprehnsive study of silica NPs under Lyman alpha radiation, i.e.,
Dark matter does not exist because cosmic dust that permeates the Universe redshifts galaxy light thereby overstating the recession and rotational velocity of galaxies to give the impression the Universe is expanding faster than expected and dark matter is required to hold rotating galaxies together.
The redshift in cosmic dust went unnoticed for almost a century because the light-matter interaction of galaxy light was assumed to follow classical physics allowing the heat capacity of the nanoscopic dust to conserve the galaxy photon by an increase in temperature. But the heat capacity of the atom given by the Planck law of QM is not scale invariant being finite at the macroscale while vanishing at the nanoscale. QM stands for quantum mechanics. Conservation of the galaxy photon is therefore only possible by a non-thermal light-matter interaction mechanism proposed here to be simple QED.
Simple QED relies on the high S/V ratio at the nanoscale whereby the galaxy photon of wavelength λo is absorbed almost entirely in the dust surface placing internal atoms under the high EM confinement necessary in the Planck law of QM for heat capacity to vanish. S/V stands for surface to volume. A non-thermal EM standing photon having half-wavelength λ/2 = d is then created as the galaxy photon energy adjusts to the EM confinement bounded by the dust surface. The speed of light c corrected for the refractive index n of the dust gives the energy E of the redshift photon, E = h(c/n)/λ for a wavelength 2nd and redshift Z = (2nd - λo)/ λo. Once the energy of the galaxy photon absorbed in the dust surface is expended to form the standing photon, the EM confinement vanishes and the galaxy photon now redshifted is free to travel to the Earth. See Abstract
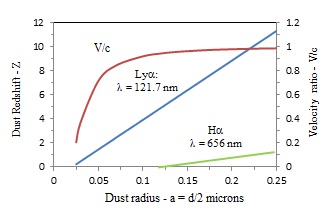
The following redshift Z for Lyman and hydrogen - alpha galaxy photons in cosmic dust may approach the speed of light significantly overstating galaxy velocities that have erroneously been interpreted as dark matter.
In conclusion, correcting measured galaxy redshifts for cosmic dust, not only does dark matter need not exist, but both GR and scale invariant GR are irrelevant as galaxy dynamics follows Newtonian mechanics. See Presentation Press Release. and Presentation
An MP3 Audio file of the presentation is available. Open the Presentation PPT and Audio files in separate windows and manually adjust the PPT file to follow the Audio file.

In the early twenties of the last century, Alexander A. Friedmann (1888-1925) derived from the system of ten Einstein's equations applied to a perfectly symmetric universe, which is homogeneous and isotropic for every fixed time instant, a nonlinear differential equation for the expansion rate of the universe. The question is whether one can perform such excessive extrapolations, i.e. to apply Einstein's equations to galactic or cosmological scales. The current standard model of cosmology is based on the normalized Friedmann equation which contains, as major parameters, densities of dark matter and dark energy. So, it is timely to gather specialists from different disciplines, including galaxy evolution and planetology, to discuss the problem of existence of dark matter and dark energy at various scales, both from theoretical and observational points of view.
In this regard, the topic of interest to be presented focusses on the Hubble measurement of Universe expansion that provided the experimental basis foe Einstein's equations. Specifically, whether Hubble's redshift measurements did indeed show Universe expansion in the presence of the ubiquitous cosmic dust. My paper is:
Cosmology and redshift in cosmic dust.
See Abstract and Presentation
An Audio MP3 file of the PPT Presentation is available. Open both in separate windows and follow the PPT with the Audo file.

by
Zero Point Energy or simple QED?
In 1913, Einstein and Stern developed the concept of zero point energy, or ZPE. However, the reality of ZPE as a source of energy still questioned today. Recently, ZPE at MeV levels has been proposed to explain the bursts of X-rays observed in LENR upon the glow discharge heating of a palladium Pd cathode even after the discharge ceases. LENR stands for low energy nuclear reactions.
The observation of 1-6 keV X-rays in glow discharge of palladium Pd cathodes from 1 eV plasmas is not explained in the literature. Nuclear reactions as a source of diffuse X-ray emission that require MeV plasmas are not possible in 1 eV glow discharge while a collimated X-ray mechanism is not known to produce a 20 μs burst duration every 50 μs present up to 20 hours after switching off the glow discharge.
In 1900, Planck explained the radiation spectrum of a black body by treating the absorption of energy as discrete and not continuous. Apparently, Planck did not consider the energy between quantum levels as a temporary state depending on the amount of heat absorbed from the surroundings and treated the absorbed heat as the average energy Eav between (n -1) and n quantum levels,
Eav = ½ [ nhν + (n - 1)hν ] = ½ [ 2n - 1 ] hν.
In the ground state, n = 1, and therefore Planck defined the ZPE = ½ hν. However, this is a problem because the energy supplied to an atom may have any value, i.e., ZPE < hν and most likely not ½ hν. Since ZPE < X-ray level, the ZPE at MeV levels cannot not exist.
Instead, the X-ray bursts in glow discharge are produced by the simple QED quantum state which is a consequence of QM that by Planck's law requires the heat capacity of the atom to vanish under high EM confinement. QM stands for quantum mechanics. Heat capacity vanishes because atoms have high surface-to-volume ratios that require the heat Q to almost entirely be deposited in their surface. Precluded from thermal expansion, the surface heat places the atom under the high EM confinement necessary by the Planck law for heat capacity to vanish.
Absent heat capacity, the atom cannot conserve the heat Q by an increase in temperature. Instead, the simple QED transition from the ground to X-ray levels is made by converting the heat Q in the surface to non-thermal EM energy in the form of standing photons inside the atom having half-wavelength λ/2 = 2r, where r is the atomic radius. The Planck energy E of standing photons is, E = hν = hc/λ = hc/4r, where c is the speed of light. If the heat Q is sufficient to reach the X-ray level, the X-ray is emitted. But if not, the heat Q briefly resides in a temporary state of the atom only to be promptly re-emitted as EM radiation at frequency ν to recombine with emission from other atoms and allow the transition to X-ray levels.
The X-ray emission from glow discharge with a Pd cathode is reproduced in the following figure.
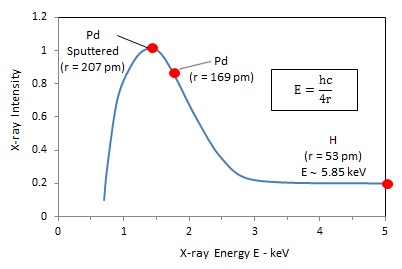
For Pd atoms having radius r = 169 pm, simple QED gives E = 1.83 keV and wavelength λ = 0.676 nm. Experimentally, the X-ray peak occurs at a lower energy of 1.5 keV because sputtering produces clusters of Pd atoms not having radii exactly 169 pm, i.e., not perfectly bare Pd atoms. The heat flow Q is approximated as the classical heat flow Q from the glow discharge cathode temperature T into the atoms in the nearby plasma as, Q = πHr^2T, where H =5.67 W/m^2K is the natural convection heat transfer coefficient, and T the cathode temperature. Assuming T = 1 eV = 11,500 K, Q = 5.85 x 10^-15 J/s. The time for an individual atom to reach the X-ray level is, τ = E/Q = 50 ms. But X-ray transitions require τ < 150 fs and the heat Q = 5.85 x 10^-15 J/s is not sufficient. The required heat flow Q > Q*, where Q* = E/150 fs = 1.95 x10^-3 J/s.
To emit X-rays at heat flow Q < Q*, a cooperative effect is required. In a collection of Nt atoms, simple QED as a variant of the Dicke state is proposed to produce collimated superradiant X-ray emission in the direction of the heat flow Q. Unable make the X-ray transition at heat flow Q, each atom spontaneously re-emits Q as EM radiation at frequency ν that upon recombination with that from other atoms produces the required heat Q* to make the X-ray transition in a smaller number N of atoms. In (Fig. 4(b) of [2]), N is the number of collimated X-ray photons/burst ~1.6 x 10^8. Hence, each X-ray photon is produced by 50 ms/150 fs ~ 3.33 x 10^11 atoms, or only a very small fraction of the Nt atoms emit X-ray photons. When the glow discharge is turned off, the atoms are only heated by the temperature Tc of the residual heat in the cathode that slowly decays. Although Tc < T, the heat Q decreases, but the number N of X-rays adjusts accordingly and X-rays may still be observed.
In conclusion, simple QED as a variant of superradiance explains X-rays in LENR without any need for the ZPE or nuclear reactions. See Abstract and Press Release
In QED, Feynman [1] proposed virtual protons produce real phenomena. QED stands for quantum electrodynamics. But QED mediates light-matter interactions with virtual photons and cannot be verified experimentally. Even Feynman's argument that light is made of virtual particles is conjecture as any theory of light-matter interaction can only be verified if based on real photons.
The problem with wave-particle duality is a mechanism is not known for how the photon as a particle becomes a wave. Given the Universe is comprised of matter that exists in all sizes from planets to atoms, the hypothesis is made that the photon as a wave may only be revealed upon the interaction of a particle with size dependent matter.
Simple QED is proposed as the mechanism by which heat controls the interaction of a particle with matter. Differing from Feynman's QED, simple QED mediates the interaction with real photons. The heat content of matter is based on Planck's law of QM that defines the heat capacity of constituent atoms to depend on EM confinement. Atoms in macroscopic matter absent EM confinement follow classical physics and conserve the heat of particle by increasing the temperature of matter. But QM differs from classical physics in nanoscopic matter.
In matter at the nanoscale, say in a NS comprising a number of atoms, the heat capacity vanishes because the high surface-to-volume ratio requires the heat of the particle interaction to almost entirely be absorbed in the NS surface. NS stands for nanostructure. Absent heat capacity, the surface heat cannot increase NS temperature. Precluded from thermal expansion, the surface heat places NS atoms under the EM confinement required by the Planck law for the capacity to vanish. Conservation of surface heat therefore proceeds by simple QED creating non-thermal EM standing waves in the NS having half-wavelength λ/2 = d, where d is the minimum NS dimension. The Planck energy E of the standing waves is, E = hν = h(c/n)/λ = hc/2nd, where h is Planck's constant, c is the speed of light, and n the refractive index of the NS. Typically, a NS having dimensions d < 100 nm have simple QED frequencies ν in the EUV.
Simple QED is a new quantum state depending only on the size of the NS that defines the EM energy of the standing wave. Quantum levels of constituent NS atoms having UV-VIS-IR states including plasmon resonances are excited from the simple QED state by EUV fluorescence. Absent lower NS states, the simple QED photon is emitted at frequency ν to the surroundings. In astronomy, simple QED allows the particle emitted from a distant star with Planck energy E = hν* to be redshift upon interacting with a NS of cosmic dust to produce a lower emission frequency ν, i.e., ν < ν*. With X-rays > 1 keV, the NS is required to fragment to atomic dimensions with simple QED giving the Planck energy E = hc/4r, where r is the atomic radius.
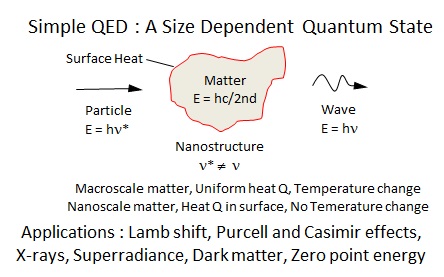
Simple QED is applicable to a wide range of diverse phenomena shown in the above figure, a few applications are presented as follows.
X-ray emission by ZPE The X-ray emission from 1-2 kV glow discharge with a Pd cathode thought caused by zero point energy or ZPE is superseded by superradiance from simple QED having energy levels depending only on the size of the atom. But X-ray transitions require heat Q* = E/τ to be deposited in τ < 150 fs. To emit X-rays at heat flow Q < Q*, a cooperative effect is required. Similar to the Dicke state, simple QED for a collection of atoms produces collimated superradiant emission in the direction of the heat flow Q from the cathode. See PressRelease
Perseus 3.5 keV X-rays The mysterious 3.55 keV X-ray emission from the Perseus galaxy cluster not present in emission lines of atomic elements thought caused by dark matter is also superseded by simple QED . Applying simple QED to the 3.55 keV X-ray emission gives wavelength λ = 0.349 nm. The atom diameter d = λ/2n, but at X-ray frequencies, n = 1 and d = λ/2 = 174.5 pm with radius r = d/2 = 87.25 pm. Of the atomic elements, krypton and sulfur have radii = 88 pm. Krypton aside, simple QED emission is consistent with X-rays produced in laboratory charge-exchange experiments for bare sulfur atoms. See Press Release
In conclusion, simple QED explains light-matter interaction by wave-particle duality with real photons. A wave only exists as the Planck energy of the particle is conserved in the interaction with matter, the wave properties depending on the size of matter. Only the Planck energy of the particle interacting with matter is important, the structure of the particle as viewed by Feynmen is not important. Therefore, in a vacuum, the photon as a particle has the Planck energy E = hν* and remains a particle until interacting with matter such as cosmic dust at which time becomes a wave having frequency ν*. See PressRelease
Confirmation of Cosmic dust as dark matter
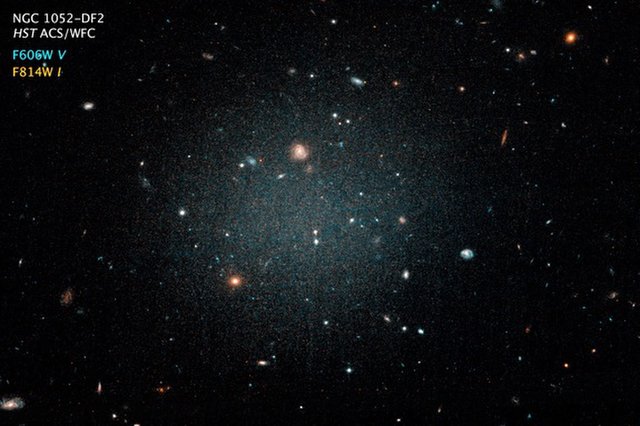

The DF2 galaxy containing globular galaxy clusters was recently reviewed for the presence of dark matter. As shown above, DF2is a transparent galaxy with galaxies in the background shown to be visible. Dark matter was inferred from the velocity V of the clusters, i.e., fast moving clusters suggesting dark matter is present in holding the clusters together, but if slow moving, dark matter need not exist. Cluster velocities were inferred from the Doppler effect using redshift Z from absorption lines of the calcium triplet state. For Z <<1, the galaxy velocity V ≈ Z*c, where c is the velocity of light. On this basis, dark matter in DF2 was not found because high cluster velocities V common to galaxies thought to have dark matter were not measured.
Missing dark matter in the DF2 galaxy poses a conceptual dilemma to modern cosmology that claims dark matter permeates the Universe. Although other explanations are possible, some astronomers argue DF2 rules out MOND as an alternative explanation for dark matter. MOND standing for modified Newtonian dynamics claims dark matter is not real but an illusion, caused by our lack of knowledge of gravity on large scales. However, dark matter should always be detected independent of galaxy transparency, as it is a consequence of ordinary matter, and therefore DF2 does refute MOND as an alternative theory to dark matter. PressRelease
The DF2 galaxy not only marks the demise of dark matter in cosmology, but also the alternative explanation of dark matter by MOND. An alternative dark matter theory to MOND is suggested based on the transparency of a galaxy cluster that distinguishes DF2 from other galaxies.
The proposal is dark matter is not real, but rather an overstatement of measured velocities of galaxy clusters that includes redshift by cosmic dust giving the impression dark matter mass must be present to hold the cluster together. If the Universe were in fact transparent like DF2, the velocity of a galaxy inferred from the redshift of light by the Doppler effect shift would be correct. But cosmic dust permeates the Universe, and therefore correct galaxy velocities require correction for redshift in dust.
In theory, redshift of galaxy light in cosmic dust is a consequence of light-matter interaction of a single galaxy photon with a nanoscopic dust particle, as multiple interaction of galaxy photons with the same dust particle are unlikely. The interaction of the galaxy photon as a real photon is described by simple QED unrelated to the complex theory of virtual photons proposed by Feynman. Simple QED is a consequence of QM that by the Planck law requires the heat capacity of dust to vanish under high EM confinement induced by high S/V ratios that requires heat to be deposited almost entirely in the dust surface. QM stands for quantum mechanics, EM for electromagnetic, and S/V stands for surface-to-volume. Since QM denies dust atoms heat capacity, the heat of the galaxy photon absorbed in cosmic dust does not increase temperature. Precluded from thermal expansion, the surface heat places internal dust atoms under the high EM confinement necessary heat capacity to vanish.
Absent conservation of the galaxy photon by temperature, simple QED converts the heat in the dust surface to non-thermal energy of a real photon defined by the dimensions of EM confinement between opposing dust surfaces. For a spherical dust particle, the simple QED photon standing inside the dust has half-wavelength λ/2 = d, where d is the dust diameter. The Planck energy E of the simple QED photon is, E = hν = h(c/n)/λ = hc/2nd, where c is the speed of light with the refractive index n correcting for the lower light speed in the dust. Upon the galaxy photon adjusting to the EM confinement of the dust particle, the simple QED photon may be red or blue shifted depending on the dust size. However, the absorption of a single galaxy photon only allows redshift as blue shift is precluded by energy conservation. Once the surface heat is expended in forming the simple QED photon, the EM confinement vanishes and the simple QED photon is free to travel to the Earth as a redshifted galaxy photon. For diverse applications of simple QED see: http://www.nanoqed.org/, 2010 – 2018.
In applying simple QED to the redshift in cosmic dust, the dust redshift Z is given by Z = (λo - λ)/λ, where λo = 2nd is the wavelength of the galaxy photon observed on Earth. The redshift Z is computed for the Lyman-alpha (Lyα) and Hydrogen-alpha (Hα) lines in relation to the radius r of cosmic dust, r = d/2. The error in velocity V caused by cosmic dust is observed to approach the speed of light c depending on dust size. Since the redshift of individual Lyα and Hα lines is required to be the same for all galaxy velocities, the corrected redshift Zc to the measured redshift Zm is,
Zc = Zm - ( Z Lyα – Z Hα )
If Z Lyα = Z Hα, then Zc = Zm and galaxy velocities V given by the Doppler effect are valid, but otherwise the velocities V are invalid by cosmic dust.
In conclusion, if the measured redshift is corrected for the redshift in cosmic dust, there is no need for dark matter to explain an expanding Universe or the rotation curves in spiral galaxies suggesting the Universe is dynamic, but otherwise static and infinite. PressRelease
Dark Matter:It's the redshift in cosmic dust,stupid!

The transparent DF2 galaxy containing globular galaxy clusters was recently reviewed for dark matter based on the velocity of the clusters inferred from redshift of the calcium triplet (CaT) absorption line, i.e., fast moving clusters suggesting dark matter is present in holding the clusters together, but if slow moving with velocities following Newtonian mechanics, dark matter did not exist. On this basis, DF2 was concluded to not contain dark matter, the consequence of which is significant because cosmology is based on the premise that dark matter permeates all of the Universe. Even MOND, an alternative explanation for dark matter based on gravity, is also refuted by DF2 because like dark matter, gravity throughout the Universe should not depend on galaxy transparency. MOND stands for modified Newtonian dynamics.
But what is it about dark matter that has led to the current dilemma in modern cosmology?
Since Hubble, astronomy has unequivocally claimed the velocities of distant galaxies are given by the redshift of light emission from the galaxy, although Hubble himself questioned the validity of his measurements. In this regard, dark matter may not be real, but rather an overstatement of velocities of galaxies because of the additional redshift by cosmic dust before being measured on Earth. If so, the notion that dark matter must be present to hold the cluster together is simply invalid. If the Universe were in fact transparent like DF2, Hubble's measurement of galaxy velocities inferred from the redshift of light would have been correct. But cosmic dust permeates the Universe, especially surrounding galaxies, and therefore valid velocities require corrections for redshift in dust, a correction Hubble did not make. See Press Release
The DF2 galaxy lacking dark matter is characterized by transparency, but in the Universe, transparency in galaxies is not new. Indeed, transparency in UDG has been known for some time. UDG stands for ultra-diffuse galaxies having a near spherical shape. Recently, distant UDG have been shown to have the signature of the absence of dark matter. Similarly, high-redshift spiral galaxies from about 10 billion years ago have been reported that show the outer disk to be transparent, although the bulge is opague. Unlike the flat rotation curves common in nearby spiral galaxies, the high-redshift spiral galaxies have rotation curves that decrease with increasing distance from the bulge suggesting the dark matter is negligible.
Cosmic dust as the explanation why UDG and high-redshift spiral galaxies do not have a dark matter signature is based on the lack of dust between the galaxy and the observer. Typical galaxy transparency is depicted in the contrast between the transparent DF2 galaxy (upper) and an edge-on view of the NGC 891 spiral galaxy (lower) shown above. The spiral galaxy shows a thick disk of debris and dust darkened by high opacity, but in the vertical directions is transparent evidenced by bright background stars. The dust darkening is greater from the receding edge to the central bulge than from the approaching edge to the bulge because of the dispersion in the trailing dust. Since dust redshift in the receding region is greater than in the approaching region, the rotational velocity curve is usually plotted from the bulge to the receding edge as the average of both regions.
What this means is rotational velocities of NGC 891 inferred from redshifts of galaxy light passing through the dust are far greater than predicted by Newtonian mechanics. Moreover, the redshift of galaxy light passing through the receding region may be considered uniform from the bulge to the receding edge giving a flat rotation velocity curve. Conversely, the absence of cosmic dust from the UDG and the outer disk of high-redshift spiral galaxies allows galaxy dynamics to be governed by Newtonian mechanics. Since high-redshift determined from the bulge is most likely also caused by cosmic dust, the galaxy as a whole is actually nearby and not a relic from 10 billion years ago. See PressRelease
In conclusion, esoteric explanations of dark matter abound the literature only because galaxy velocities based on redshift were, and still are taken as dogma in cosmology, i.e., MOND, Higgs, scale invariance, etc. Perhaps, astronomy should consider the possibility that dark matter is simply the consequence of an incorrect dogma of galaxy velocities questioned by Hubble almost a century ago.
One such possibility is the redshift in cosmic dust. If indeed, galaxy redshift is corrected for cosmic dust, there is no need for dark matter to explain an expanding Universe or the rotation curves in spiral galaxies because galaxy dynamics would be simply governed by Newtonian mechanics.
not the shape of rotation curves!
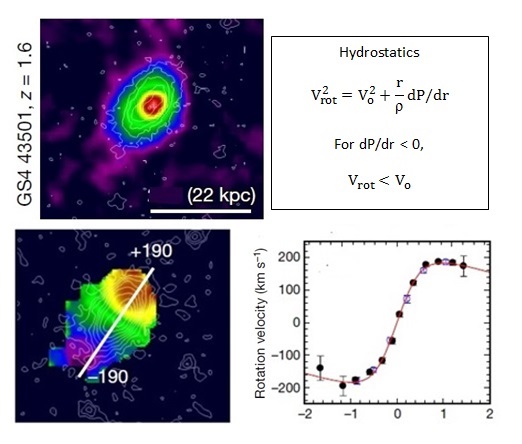
Cold dark matter cosmology is based on galaxies of stars, gas , and cosmic dust embedded in surrounding halo of dark matter. In the local Andromeda (M31) galaxy having low-redshifts (Z < 0.001), the mass of dark matter within a galaxy disk increases with disk radius becoming dominant in the outer disk producing flat rotation velocity curves which have been interpreted as the signature of dark matter.
However, high-redshift (0.6 < Z < 2.6) galaxies in the distant Universe from about 10 billion years ago were recently found to have falling rotation curves. The redshift intensity plot of the Hα line for GS4 43501 is shown in the upper panel of the above figure. The bulge intensity shown in red corresponds to a maximum redshift Z = 1.6 with minimum Z < 0.6 at the outer disk edge noted in purple. The lower panel shows the rotation velocities along the direction of the white line. Unlike the flat rotation curves common to local galaxies, distant galaxies appear to have falling rotation curves, at least for short distances. Regardless, modern cosmology that relies on the invariance of dark matter permeating both the local and distant Universe is placed in question by an unexpected redshift dependence.
In this regard, high-redshift galaxies were thought baryon-dominated, with dark matter playing a smaller part in the falling rotation curves than in the local Universe; and second, the large velocity dispersion of turbulence in high-redshift disks introduces a substantial pressure term that leads to a decrease in rotation velocity with increasing radius. In the upper panel of the above figure, the Bernoulli equation gives the rotational velocity Vrot = Vo of the gas if the pressure term dP/dr vanishes. Therefore, to explain the falling rotation curves in high redshift galaxies, a substantial pressure term dP/dr < 0 is required to reduce the rotation velocity Vrot < Vo. But this argument is problematic. Pressure does not exist in the vacuum of space to justify the claim that rotation velocities are reduced by gas pressure. In optically thin gas disks, collisions between gas molecules do transfer momentum, but this has nothing to do with pressure in the continuum implicit in the Bernoulli equation.
Since the 1970's, dark matter was thought to exist because the rotational velocities found in Andromeda M31 and other galaxies having redshift Z < 0.001 were higher than expected by Newtonian mechanics which suggested the galaxies could not be held together as they appear. Following Hubble's methodology, the rotation velocities were inferred from the redshift of spectral emission from the galaxy, the consequence of which was flat rotation curves are the signature of dark matter holding M31 together. But the redshifted galaxy light undergoes an additional redshift upon absorption in the cosmic dust that concentrates at the outer edge of spiral galaxies. Since the redshift in dust significantly overstates the rotation velocities, the premise that dark matter must be present to hold the M31 galaxy together is therefore false.
But the same argument may be made for the distant GS4 43501 galaxy as the figure shows falling rotation velocities < 150 km/s are similar to M31. Hence, dark matter is still necessary to hold GS4 43501 together. What this means is cosmic dust is overstating the velocities of ALL rotation velocities in both low and high-redshift galaxies. See above "Ghost galaxy: Evidence for cosmic dust as the source of dark matter"
In near and far galaxies, the shape of the rotation curves has nothing to do with the existence of dark matter. Both flat and falling curves have rotation velocities < 150 km/s which still require dark matter to hold the galaxies together. See above "It's the redshift in cosmic dust, stupid!".
Nearby Galaxies Cosmic dust concentrates at the outer edge of nearby galaxies to increase the redshift in the spectral line emissions from the galaxy to significantly overstate actual velocities giving the false impression that dark matter exists to hold the galaxy together.
Distant Galaxies In high-redshift galaxies, cosmic dust makes the galaxies appear more distant than actual distances. Indeed, the redshift Z = 1.6 of the bulge of GS4 43501 shown above is grossly overstated by cosmic dust. To show dark matter exists, redshift measurements at the outer disk edge require Z << 0.001, but appear problematic.
In conclusion, the shape of the rotation curves has nothing to do with dark matter. Both near and far galaxies still require dark matter to hold the galaxies together. But if redshift in ALL galaxies is indeed corrected for cosmic dust, dark matter need not exist to hold galaxies together as galaxy dynamics is governed by Newtonian mechanics. See PressRelease
not Dark Matter
Since the 1970's, dark matter was thought to exist because the rotational velocities found in Andromeda M31 and other low-redshift galaxies (Z < 0.001) were higher than expected by Newtonian mechanics which suggested the galaxies could not be held together as they appear. Following Hubble's methodology, the M31 rotation velocities were inferred from the redshift of the nitrogen NII line, the consequence of which was flat rotation curves became the signature of dark matter holding galaxies together. However, high-redshift (0.6 < Z < 2.6) galaxies in the distant Universe were recently found to have falling rotation curves suggesting the absence of dark matter. What this means is modern cosmology faces a dilemma as dark matter should not depend on whether a galaxy is in the local or distant Universe.
Unlike the data for M31 that shows flat rotation curves out to 24 kpc, criticism of the falling rotation curve in the high-redshift galaxies is the data was only taken out to about 10 kpc - not long enough to verify the curve is indeed falling. Since extended data can be resolved by future work, the emphasis in this PR is placed on the critique of flat rotation curves in M31 and specifically, to the unanswered question posed by Rubin and Ford as to what causes the decrease in intensity of the nitrogen NII line with increasing distance from the galaxy nucleus.
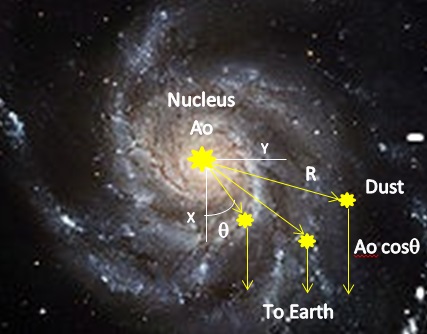
The proposal is the redshift of the NII line in M31 occurs upon absorption in cosmic dust distributed throughout the galaxy, the submicron dust particles concentrated in the outermost spiral arms. For clarity, only three dust particles are illustrated in the above figure. The dust particles are located relative to the x-axis oriented in the direction of the observer on Earth by radius R and angular position θ. The galaxy radius y is, y = Rm sinθ, where Rm is the radius locating the outermost dust particle. Ultraviolet radiation from the stars within the nucleus is assumed to produce an intensity Ao of ionized NII nitrogen at 6583 Å. The NII emission is spherical moving radially outward from the nucleus shown by yellow arrows until absorption by a dust particle which then as a local spherical emitter re-emits the redshifted NII line having at intensity Ao cosθ in the direction of Earth. The velocity V of the rotation curve is determined from the redshift Z of NII which is nearly uniform across the galaxy, but the NII intensity decreases with increasing distance consistent with observation.
Historically, the redshift in cosmic dust went unnoticed for almost a century because the light-matter interaction of galaxy light including NII was assumed to follow classical physics allowing the heat capacity of the nanoscopic dust particle to conserve the galaxy photon by an increase in temperature. But the heat capacity of the atom given by the Planck law of QM is not scale invariant being finite at the macroscale while vanishing at the nanoscale. QM stands for quantum mechanics. Conservation of the galaxy photon is therefore only possible by a non-thermal mechanism proposed here to be simple QED
Simple QED relies on the high S/V ratios of cosmic dust whereby the NII photon of wavelength λ is absorbed almost entirely in the dust surface placing internal atoms under the high EM confinement necessary in the Planck law for heat capacity to vanish. S/V stands for surface to volume. A non-thermal EM standing photon having half-wavelength λ/2 = d is then created as the NII photon adjusts to the EM confinement bounded by the dust surface. The speed of light c corrected for the refractive index n of the dust gives the Planck energy E of the redshift NII photon, E = h(c/n)/λ. On Earth, NII is observed to have wavelength 2nd with redshift Z = (2nd - λ)/λ. Once the Planck energy of NII absorbed in the dust surface is expended in forming the redshifted NII, the EM confinement vanishes and the redshifted NII is free to travel to the Earth. See PressRelease
In conclusion, The low-redshift M31 galaxy having a flat rotation curve is the consequence of redshift of the NII line in cosmic dust particles which requires the intensity of the NII line to decrease with the distance from the nucleus.
High-redshift galaxies showing falling rotation curves are more compact than M31, but otherwise mostly transparent and void of cosmic dust.
Flat galaxy rotation curves depend solely on cosmic dust having nothing to do with dark matter allowing galaxy dynamics at both low and high redshift to be governed by Newtonian mechanics.

Neuro-degenerative diseases including Autism are characterized by the proliferation of cells from mutations of the neuron's DNA sequence. The DNA damage may be caused by exposure to exogenous agents such as UV radiation or the endogenous source of oxidative stress in internal body tissue. Except for the skin exposed to exogenous solar UV, DNA damage is generally thought caused by oxidative stress. Indeed, oxidative DNA damage has been detected in brain tissue of schizophrenic patients, the consequence of which is the deficient repair of DNA that contributes to degenerative disease.
But what is the source of oxidative DNA damage?
Science has not yet recognized DNA damage from UV radiation in internal body tissue that are the source of oxidative DNA damage. But the implications of Autism from large quantities of aluminum NPs found in the brain changes this paradigm. NPs stand for nanoparticles. What this suggests is the NPs are producing the UV that creates the oxidative DNA damage, i.e., oxidative DNA damage is actually UV induced DNA damage.
Nevertheless, a causal relation between NPs and UV radiation is required.
Only recently, the causal relation of cancer from GM food was proposed from DNA damage caused by UV radiation from NPs. GM stands for genetically modified. The NPs are created during spraying herbicides on crop fields to kill weeds, but enter the corn or soybean crop and are ingested as GM food. See PressRelease
What this means is the source of neuro-degenerative diseases from the newborn to the elderly is the DNA damage from UV radiation created by simple QED from diverse NPs that enter the body in vaccines and GM food.
In theory, NPs do not naturally emit UV, but NPs do convert heat from surrounding body tissue to UV radiation if the heat capacity of the NPs somehow vanishes. Classically, NPs at absolute zero have vanishing heat capacity, but not at finite temperatures. QM differs as the heat capacity of the atom given by the Planck law at finite emperatures does indeed vanish under high EM confinement. QM stands for quantum mechanics and EM for electromagnetic. But high EM confinement is inherent in NPs upon absorbing heat because their high S/V ratios confine the heat to the NP surface. S/V stands for surface-to-volume. NP atoms are therefore placed under high EM confinement and by QM the heat capacity therefore vanishes. Lacking heat capacity, the heat may only be conserved by a non-thermal mechanism proposed here as simple QED, but differs from the complex QED theory advanced by Feynman and others.
Simple QED conserves heat by creating non-thermal EM radiation standing across the NP diameter having half-wavelength λ/2 = d as the heat adjusts to the EM confinement bounded by the NP surface. The speed of light c corrected for the refractive index n of the NP gives the Planck energy E = h(c/n)/λ, i.e., E = hc/2nd, where h is Planck's constabnt. In application, UV-C radiation at about 254 nm is a lethal level for the DNA damage in all living systems as the pyrimidine dimers are formed that block DNA replication. Aluminum NPs in vaccines having diameter d = 60 nm and n = 2 emit UV radiation at 2nd = 240 nm near the UV-C are likely to cause Autism by mutations in the neuron's DNA. Similarly, baby food with titanium dioxide NPs having n = 2.5 and d = 50 nm emit EM radiation at 2nd = 254 nm. Extensions to Alzheimer's for titanium dioxide NPs in GM food follow similar arguments. NPs having d > 100 nm are benign to DNA damage. Of importance, NPs in vacines are the toxic source and not the vaccine itself.
In summary, Autism from NP's is a risk to the health of US citizens, not only to the newborn in vaccines, but also in baby food. In the elderly, NP's in GM food are a cause of Alzheimer's and cancer. The CDC is in charge of recommending the vaccination schedule for US children, which has grown 6,000%. CDC stands for Center of Disease Control. The CDC monitors vaccine safety and tracks the number of children with Autism in the US, i.e., from 1 in 10,000 in the 1980 's to 1 in 68 today. The following table is taken from PressRelease and Abstract
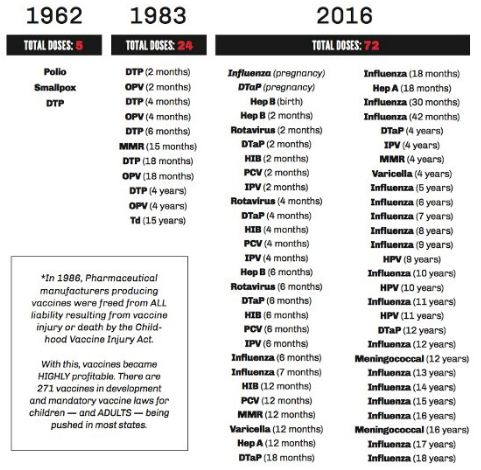
In 2016 after the US election, a group of senior CDC scientists filed an ethics complaint alleging the CDC is influenced by corporate and political interests. Collusion is suggested by the departure of the prior head of CDC - Julie Gerberding - to head the vaccine division of Merck. The scientists alleged the CDC misrepresented the rise in Autism rates since the late 1980 's a view consistent with the just elected President Trump who was quoted as saying:
When I was growing up, Autism wasn't really a factor and now all of a sudden, it's an epidemic. Everybody has their theory, and my theory is the shots. They're getting these massive injections at one time. I think it's the vaccinations.
President Trump is correct about the rapid increase in Autism from vaccinations. However, the cause of Autism is not the vaccine, but the NPs in the shots. But Trump should also consider Autism being caused from NPs in baby food which is long-term compared to short-term vaccinations as the 6,000% increase in Autism may also be linked to the rapid increase in the US of GM food containing NPs. The FDA should ban all NPs from vaccinations and food, but this is unlikely given the polarization of US politics. See PressRelease and Presentation

The IAU Conference is being held on August 28-29, 2018. Focus Meeting 10 on Nano Dust in Space and Astrophysics is of special interest because cosmic dust has mis-directed cosmology since Hubble's discovery of Universe expansion based on redshift in 1926. Currently, Universe expansion based on redshift measurements continues to mis-direct cosmology with its search for dark matter, i.e., Hubble's false notion that the velocity of receding galaxies is inferred from the Doppler effect using redshift measurements. What Hubble and subsequently many other astronomers failed to realize was that the galaxy redshift included the redshift upon absorption of galaxy light by cosmic dust on its way to the Earth. Because of this, the galaxy velocities were and still are overstated thereby supporting the false notion of an expanding Universe. Today, the overstated galaxy velocities have led to the futile earch for dark matter thought necessary to hold galaxy clusters together.
CosmoIogy has not recognized redshift in cosmic dust as the source of the false dark matter. Indeed, the scientific rationale for Focus Meeting 10 continues to rely on classical physics by treating the absorption of galaxy photons to raise the temperature of cosmic dust, i.e.,
"The presence of nano dust leads to the heating of the surrounding plasma and dusty plasma effects, like waves and instabilities...Interstellar nano dust dominates the far ultraviolet extinction as well as [producing] the near- and mid-infrared emission of the interstellar medium of the Milky Way and external galaxies"
But cosmic dust is nanoscopic and follows QM - not classical physics. QM stands for quantum mechanics. By the Planck law of QM, the atoms in the cosmic dust lack the kT heat capacity to heat dusty plasma and produce near- and mid-infrared emission of the interstellar medium. The absorption of galaxy light cannot raise the temperature of cosmic dust. Instead, conservation of galaxy light may only proceed by a non-thermal mechanism, i.e., the re-emission of redshifted galaxy light. Consequences of cosmic dust by QM in cosmology and astronomy are significant, e.g., increased dust temperatures leading to NIR and FIR spectra simply do not occur. For details, see above: The Buchalter Cosmology Prize, EWASS-2018, Light-matter interaction-Chengdu, and Nanotechnology-Rome. In this regard, perhaps the IAU Focus Meeting 10 will reach a resolution on cosmic dust by QM instead of classical physics to provide a new direction for cosmology.

Over at least the past few decades, NPs are known to cause DNA damage. But the causal relation of NPs to human health remains unknown. NPs stand for nanoparticles. Chemical reactions of NPs contacting the DNA cannot be the causal relation as DNA damage occurs even with inert NPs, the consequence of which suggests a physical causal relation. DNA damage is known caused in photodynamic therapy by high temperatures from laser heating NPs, but small temperature increases of NPs in a cell from body heat alone cannot damage the DNA.
Contrary to photodynamic therapy, heating of NPs does not cause necrosis of cancer cells from high temperatures because the Planck law of QM precludes increases in NP temperature as the heat capacity of the quantum sized NPs vanishes. Instead, the laser heat produces EM radiation within the NP beyond the UV. Unlike temperature, the UV emission suggests the causal relation of NPs to human health is therefore the well-known genotoxicity of DNA to UV radiation. Only body heat is required. The wavelength λ of the emitted EM radiation is, λ = 2nd, where n and d are the refractive index and diameter of the NP. For example, NPs having n = 1.5 damage the DNA by producing EM radiation beyond the UVC (λ < 254 nm ) for NP diameters d < 85 nm. Larger NPs are benign,
In this regard, solar UV is well-known to cause DNA damage to the skin and may lead to cancer, but cannot penetrate the skin to damage internal organs. Contrarily, NPs rescind this paradigm. Indeed, NPs by entering the body in the GM food we eat produce the low levels of UV that damage the DNA of internal organs. The DNA damage in GM food is caused by NPs included in herbicides to enhance crop yields by controlling weeds. GM stands for genetically modified.
To avoid genetic cancers in human evolution from DNA damage caused by NPs in GM food, Monsanto and other herbicide manufacturers should stop use of NPs in controlling weeds in crop fields. Otherwise, the responsible parties may be alleged guilty of a crime against humanity. See Abstract

Structural biology is the study of protein structure. The theme of the 14th International Conference on Structural Biology held on September 24-26 in Berlin is:
Of interest are the structural changes of conformation during folding and unfolding. Proteins are sensitive to electrostatic charges from amino acid side chains that change with conformation. But MD simulations of protein folding and unfolding are based on L-J force fields with electrostatic interaction represented by fixed point charges. MD stands for molecular dynamics and L-J for attractive Lennard-Jones. QM modification of point charges during conformational changes is required, but is impractical because of computational costs. QM stands for quantum mechanics.
Computation costs aside, even if point charges were indeed continuously updated, the effect on protein folding and unfolding would not be significant compared to the more fundamental QM effect of the Planck law on the heat capacity of constituent atoms. In this regard, proteins are generally thought to unfold upon increasing in temperature from heat in the surroundings, based on the classical assumption the atoms have the heat capacity to allow temperature changes to occur. But the Planck law requires the heat capacity of the atom to vanish with conservation proceeding by simple QED creating EM radiation that by the photoelectric effect removes electrons to positively charge constituent atoms. By QM, the long-held paradigm of proteins increasing in temperature is simply false. What this means is the heat thought to induce unfolding by increasing the temperature of proteins is actually conserved by producing charge that unfolds the protein by Coulomb repulsion, i.e., increasing temperature alone cannot thermally unfold a protein.
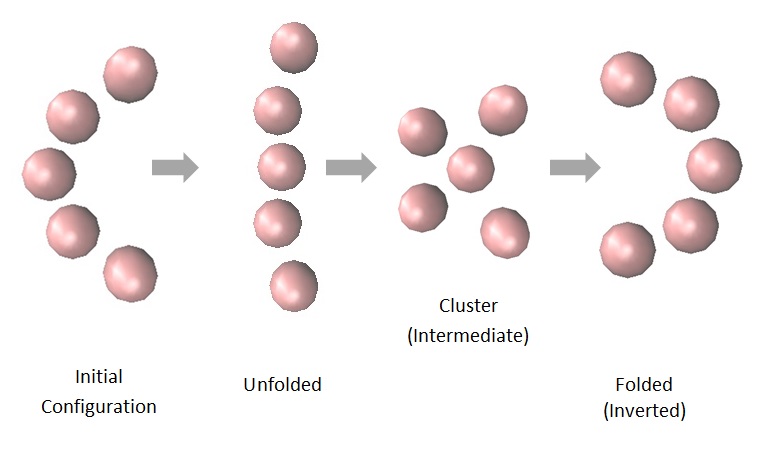
To illustrate QM induced charge, the MD simulation of folding and unfolding using Allen & Tldesley algorithms for a simple 5-atom protein is illustrated in the above figure. Time steps on the order of 0.001 fs were required to resolve the changing confirmations, the MD runs taking 10-20 million iterations. Initially, the semi-circular protein relaxes under attractive L-J forces to a cluster (not shown) but does not unfold because of a numerical bottleneck. Unfolding only occurs by breaking the bottleneck with the QM induced repulsive positive charge ( 0.5 - 1 electron charges) to each atom. The applied QM force is not steady, but fluctuates depending on the recombination time < 1 ps of electrons with charged atoms. In the simulation, the QM repulsive force was applied every 1000 iterations, i.e., every fs which is an approximation to the < 1 ps recombination time. Folding back to the intermediate cluster (shown) occurs by relaxing the protein with only L-J attractive forces without QM induced charge. The protein then returns to the semi-circular unfolded shape (although inverted) by applying the QM induced repulsive charge.
In summary, the protein naturally modifies the QM induced charge during protein folding and unfolding in the process of conserving heat by creating EM radiation instead of increasing temperature. The EM radiation removes electrons by the photoelectric effect and charges the atoms positive so as to induce Coulomb repulsion that enhances unfolding. On a pico-second time scale, the electrons recombine with charged atoms to return the protein to the folded state by placing the protein under van der Waals attractive forces. Driven by heat, protein folding and unfolding is therefore the consequence of fluctuations in constituent atoms between QM induced repulsive charged states and L-J dominated attractive states. See Abstract and Press Release